Drag the image to rotate the anatomy
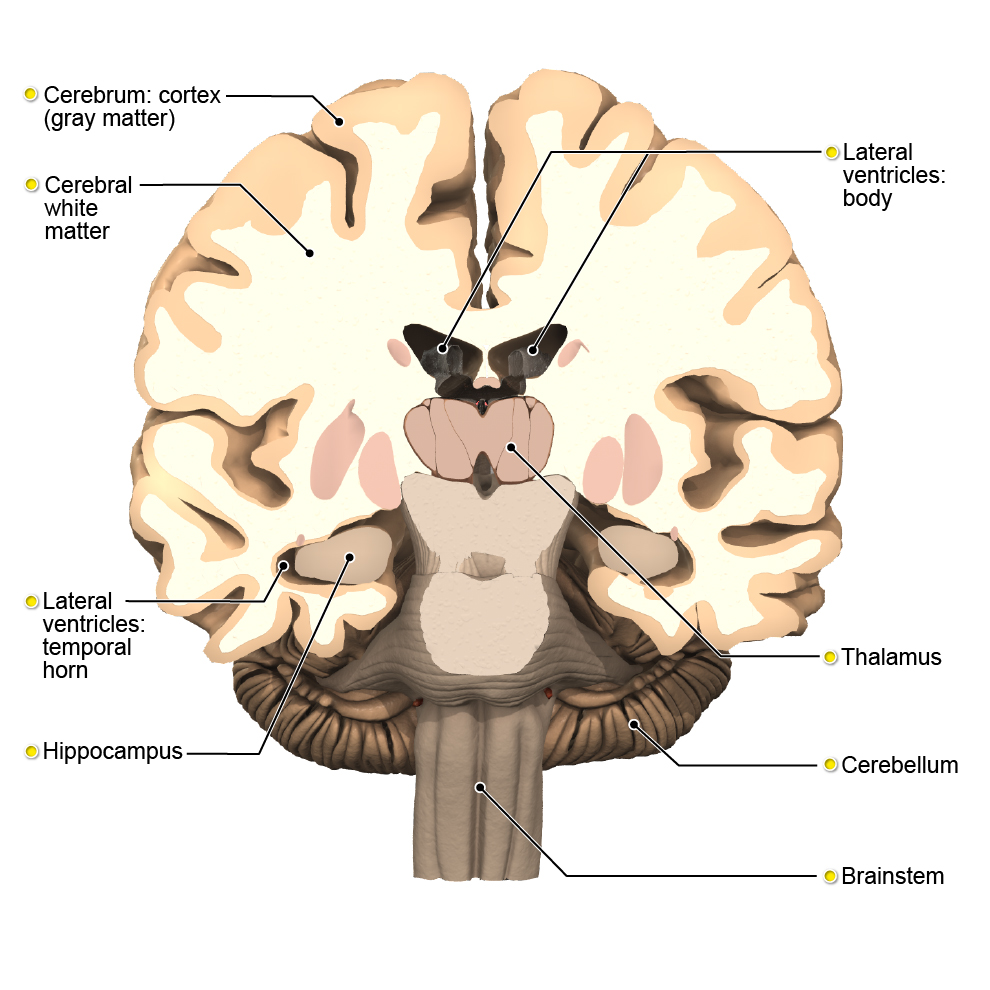
The brain can be divided into four main parts, including the cerebrum, brainstem, diencephalon and the cerebellum.
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is divided into two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes:
The cerebrum also houses the limbic system, which is the main area of the brain involved with emotion and learning. The hippocampus is an area of the limbic system found on the inner aspect of the temporal lobe. It plays a critical role in the formation of new memories.
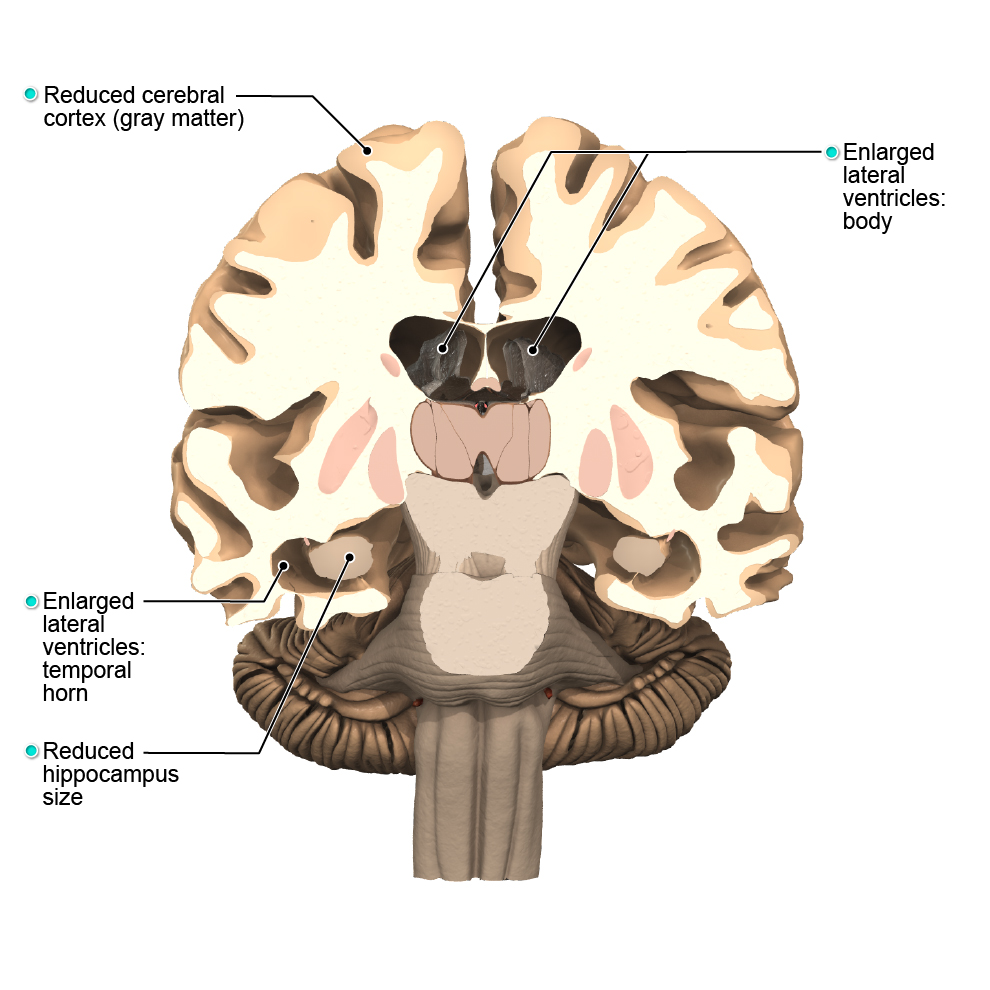
In Alzheimer’s disease brain damage, or atrophy, can occur primarily in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex. Brain damage in Alzheimer’s disease results in the gradual impairment of memory, cognitive thinking and physical abilities.
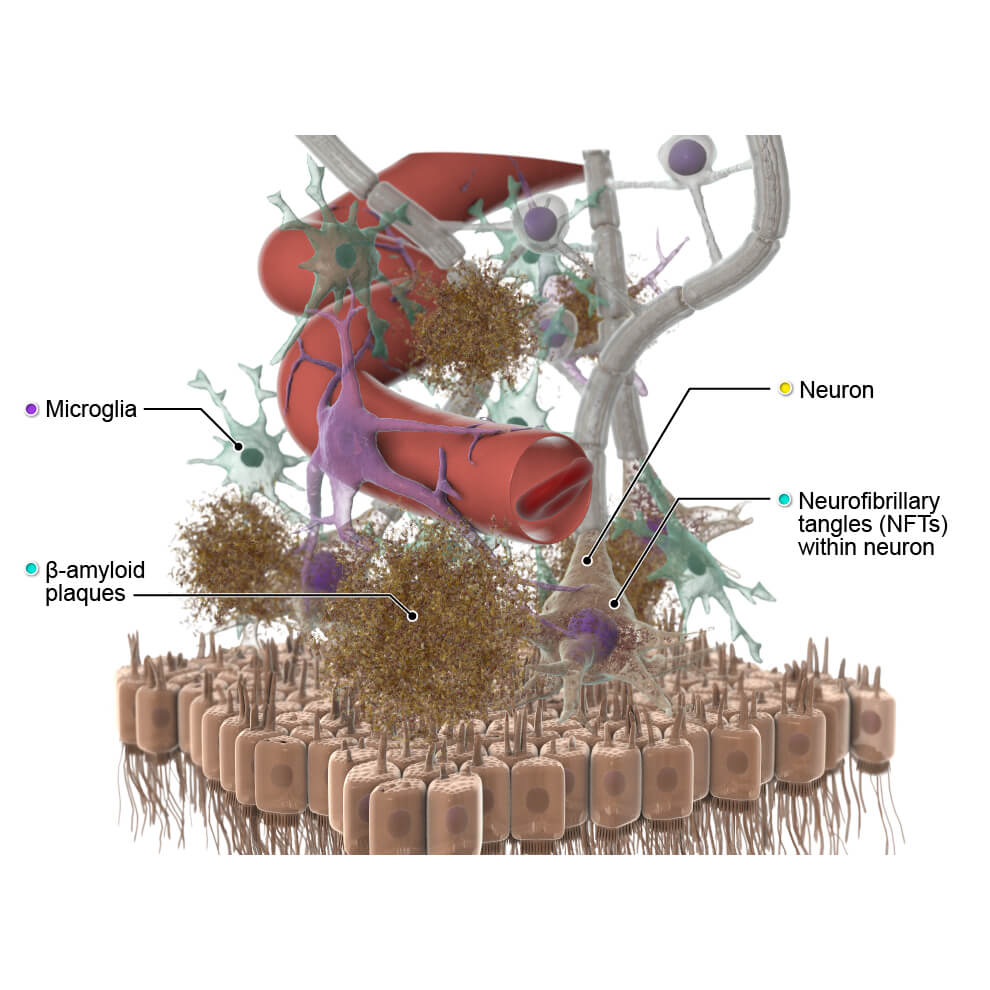
Damage is caused by the build-up of proteins called β-amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in neurons within the brain. These proteins can be toxic and may accumulate to disrupt the shape and structure of neurons.
There is currently no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, but there are several treatment options to slow down the progression of the condition and improve its symptoms: