On this page, we would like to share a small portion from our Disease & Conditions product that offers clinical content in over 70 conditions. Primal’s 3D Disease & Conditions has the potential to be an end-to-end solution for student and patient education, by showcasing our content offered in breast cancer.
Drag the image to rotate the anatomy
Invasive breast cancer is the most common type, accounting for 80% of all breast cancer cases.
Typically, abnormal cells begin to grow within the lactiferous ducts of the breast. Invasive breast cancer occurs when these abnormal cells spread outside of the lactiferous ducts to other structures in the breast.
Breast cancer is typically staged using the Tumour, Node, Metastasis (TNM) staging system, which consists of four stages.
Single tumor of <2cm found within the breast.
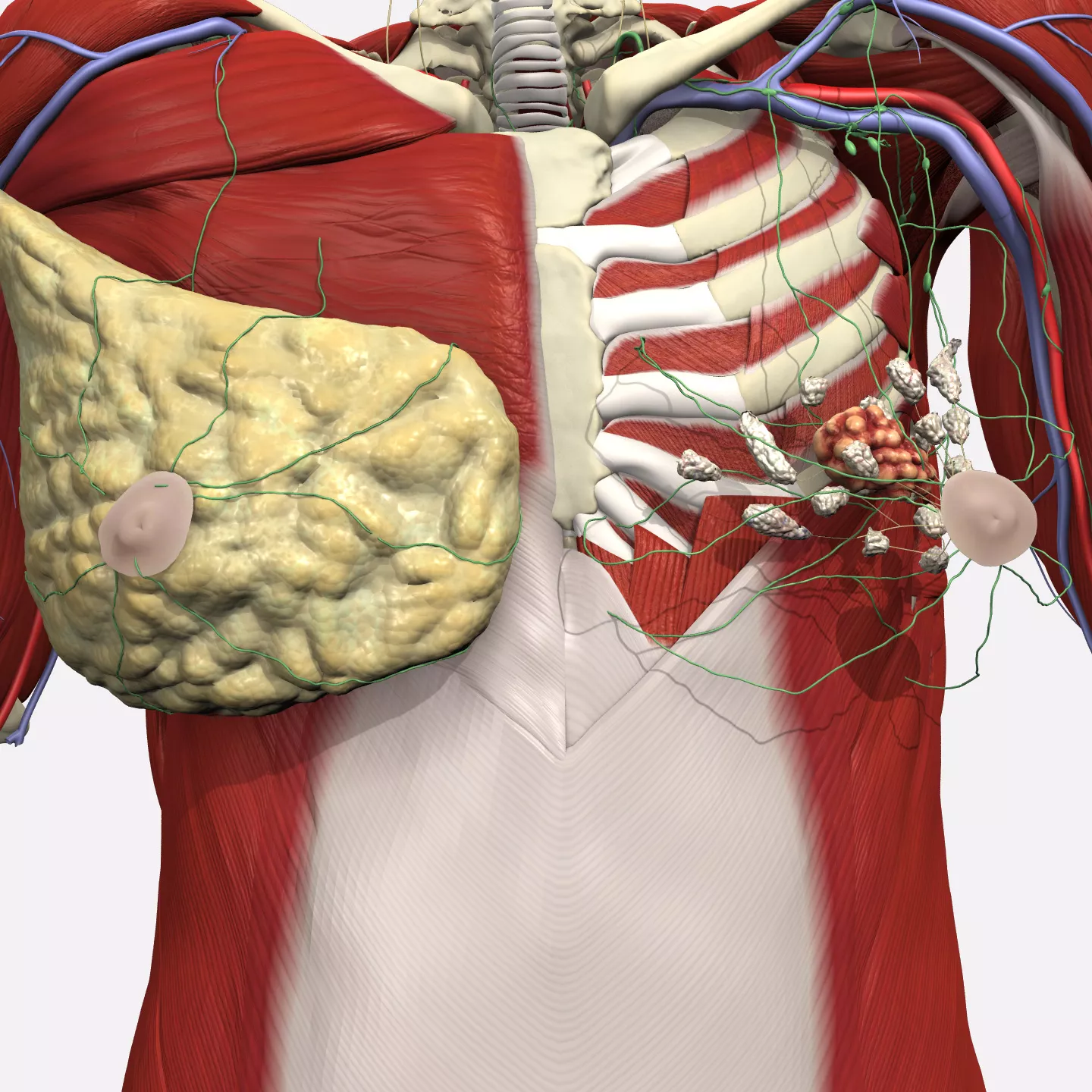
Single tumor 2-5cm found within the breast, with spread to one to three nearby lymph nodes.
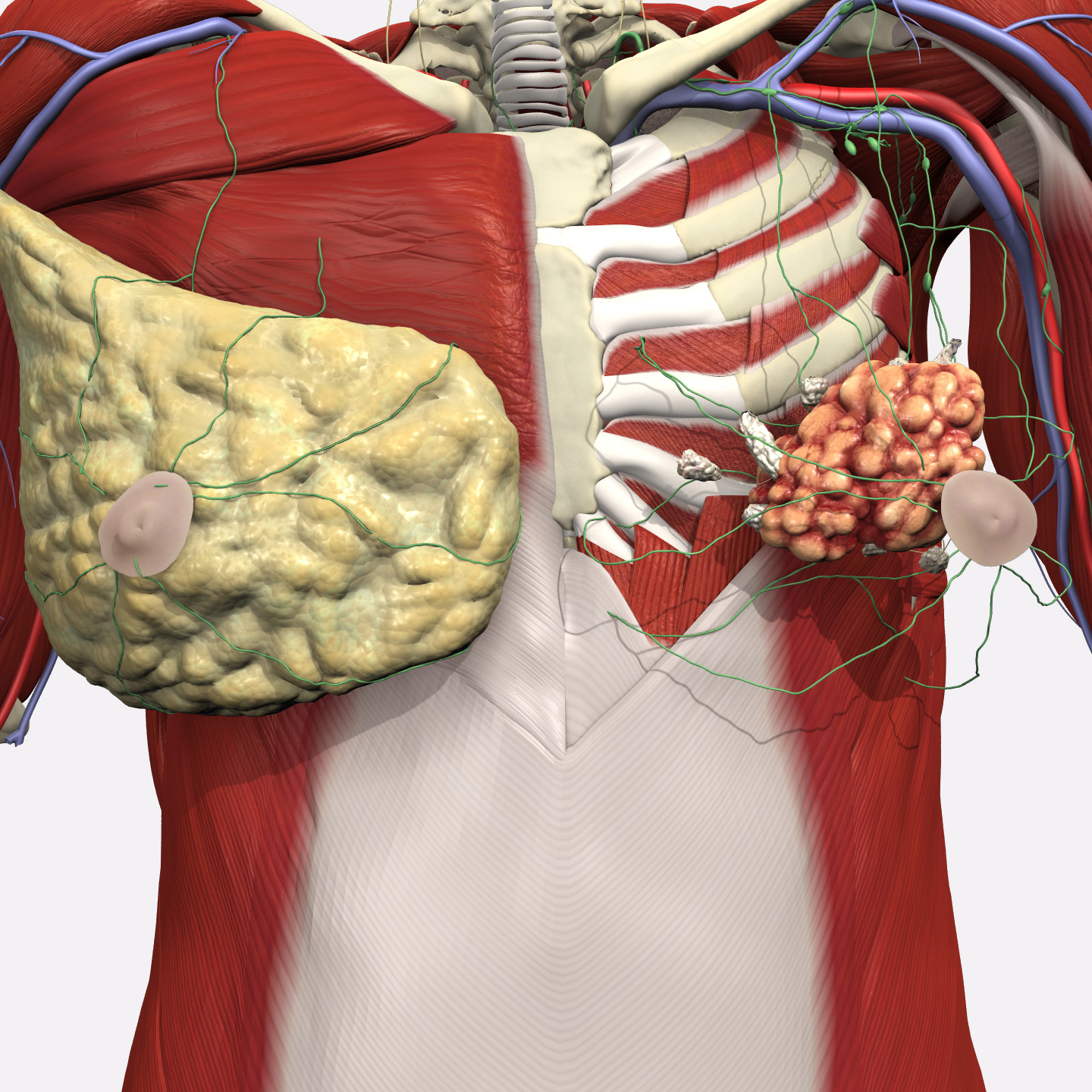
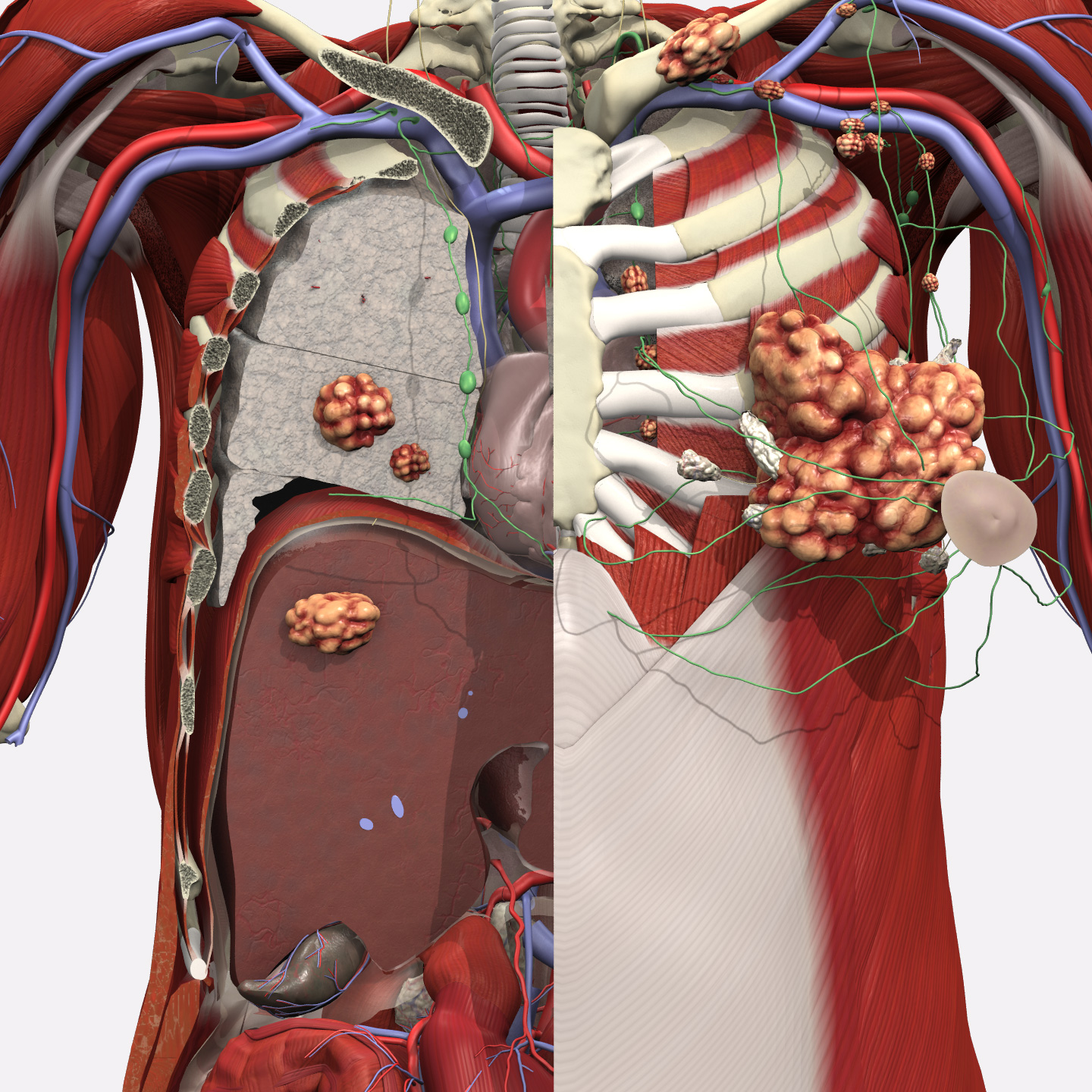
Single tumor of 1-5cm found within the breast, with spread to four to nine nearby lymph nodes. A skin rash may also appear.
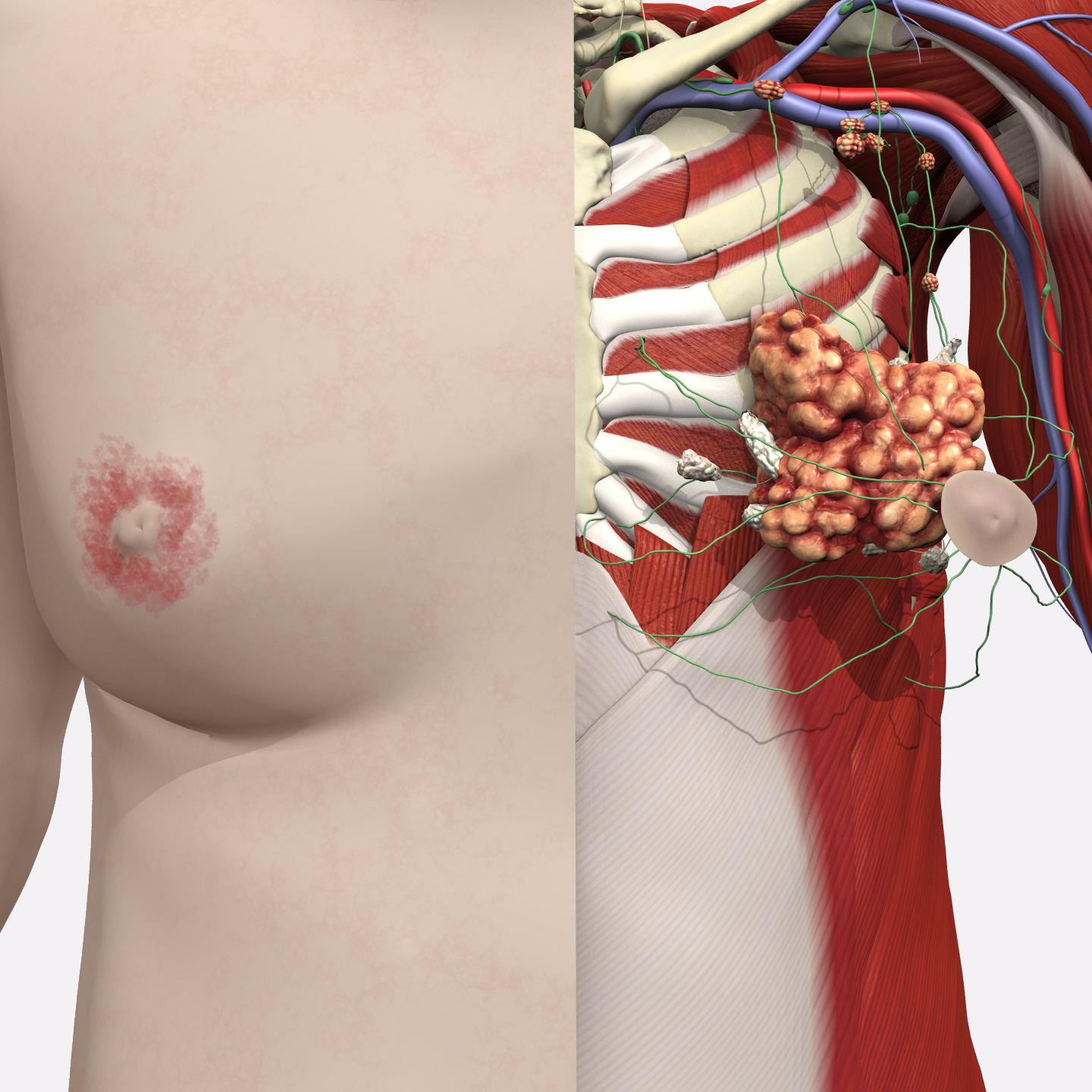
Multiple tumors found within the breast tissue, lymph nodes and distant organs such as the lungs. This is called metastasis.
Along with the staging, it is standard to test for biomarkers when a patient is diagnosed with breast cancer. Biomarkers are important because treatment may vary depending on the biomarkers displayed.
Multiple tumors growing within the breast can be felt or seen as hard lumps in the breast, changing its overall shape and size. Tumors growing within the lactiferous ducts can block their drainage and result in discharge from the nipple which may contain blood. Tumors can also grow within the lymph nodes surrounding the breast, which can result in the build-up of fluid in the breast or armpit, known as lymphedema. Blocked lymph nodes may also lead to swelling and inflammation of the skin covering the breast, giving a thickened and bruised appearance called peau d’orange.