Changing Landscape of Health Science Education
As technology becomes more affordable, available and versatile, the nature of health science education is shifting. For example, according to the American Association of Medical Schools, in 2018, more than half (56.9%) of second-year medical students reported participating in virtual pre-clerkship courses and lectures (e.g., podcast or video) either “most of the time” or “often.” This finding is similar to previous classes: in 2017 and 2016, this figure was 58% and 57.3%, respectively.
The same report also shows that second-year students’ use of online videos for their medical education information is continuing to grow. In 2018, almost one in three students (32.7%) reported using online videos on a daily basis. In 2016, the reported figure was 16.2%, or about one in six students.
Issues with Conventional Anatomy Learning
There are also pressures specific to learning anatomy around more conventional methods of exploring and understanding the human body, most notably with regard to cadavers. Rising costs and the difficulties of procuring and maintaining human specimens are an ever-present challenge, as are health and safety issues. Likewise, large student enrollments and content-packed curricula means time, or the lack of it, in cadaver lab is a growing issue.
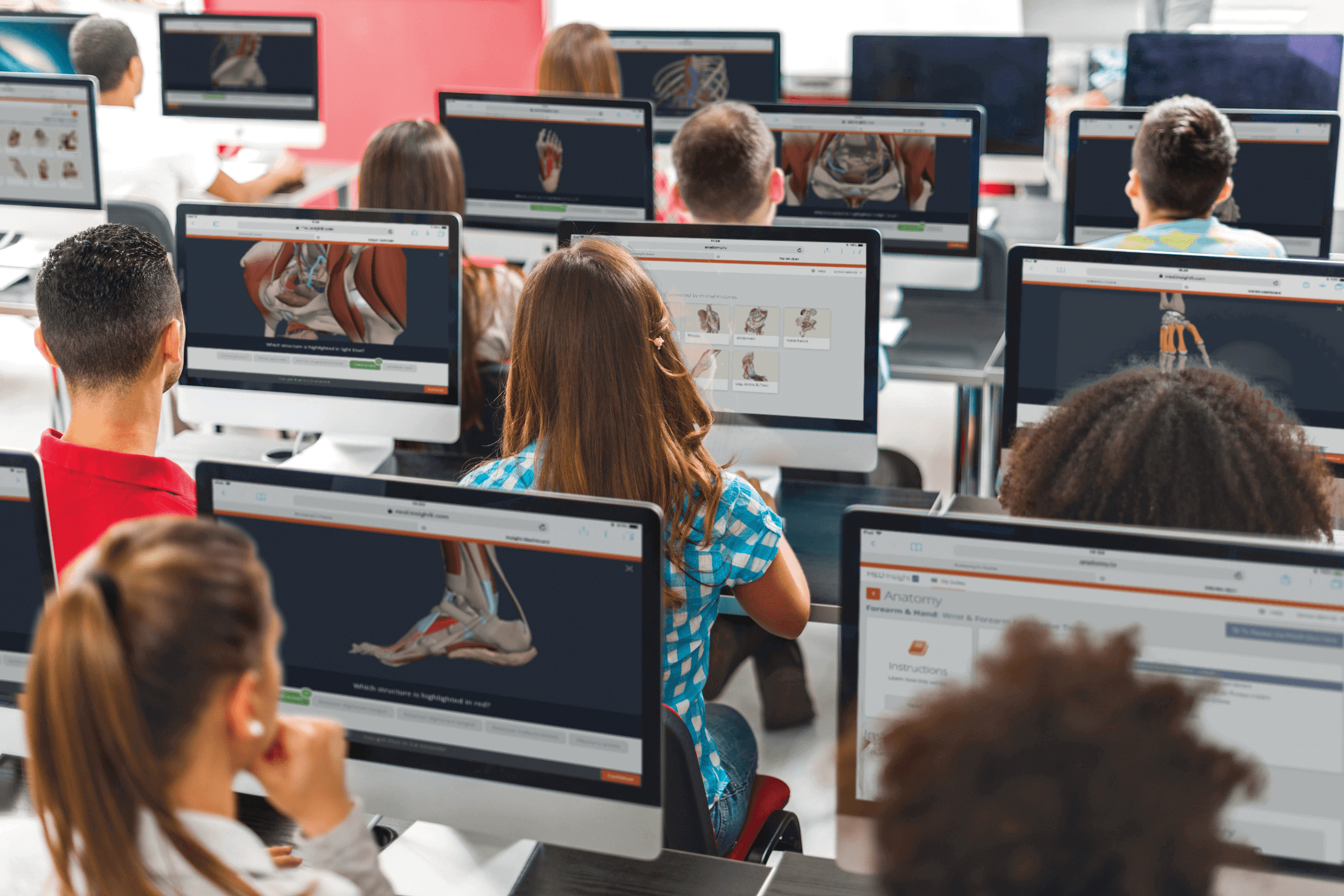
Couple this with the expectations of today’s students, and it’s no wonder that many favor digital anatomy resources as an alternative, or adjunct, to cadaveric learning. This includes an increased use of visualization through medical imaging and web-based solutions, such as our 3D interactive model.
But, as The Open University’s recent ‘Innovating Pedagogy Report 2019’ makes clear, any move to digital learning is not simply about dumping high-tech gadgets in classrooms. Indeed, digital resources alone are no substitute for high-quality teaching grounded in good curriculum.
Supporting Advances in Anatomy Pedagogy
A stronger driver of change is that as pedagogical approaches to anatomy are refined, so the likes of ‘flipped classroom’, gamification, blended and small-group learning, and the latest immersive techniques underline the advantages that digital resources deliver. For example:
- Reinforcing and expanding content
- Responding to a variety of learning styles
- Motivating students
- Developing students’ critical-thinking, problem-solving, decision-making, communication and collaboration skills
- Measuring performance
Tensions remain around what traditional dissection-based learning teaches beyond the structural and functional aspects of the human body that digital resources may not. This includes encouraging empathy and respect for future patients as part of professional development. Our experience is that digital resources can take the fear out of cadaveric dissection by providing a safe environment is which to practice. Such resources can also boost confidence in real-life clinical decision-making and practice. In addition, our 3D model is regularly used as a dissection guide in the cadaver lab, either displayed on big screens or via individual access on iPads or laptops.
Types of Digital Anatomy Resources Available
Embracing technologies for the classroom, lecture theatre, lab and private study, the ongoing focus is on mobile access via phones, laptops and tablets. Otherwise, there is a host of different types of resources out there for you to choose from. These include:
- Flashcards
- Quizzes
- e-Books
- Simulators
- 3D interactive models
- Videos and animations
- Extended reality (XR) apps across both augmented (AR) and virtual reality (VR) environments
Social media, blogs and real-time communication platforms also offer huge opportunities to explore collaborative interactive online learning experiences.
How We Can Help
Given the current breadth of choice available, what’s tricky for both educators and learners is knowing which digital human anatomy resources to trust. This is where we come in.
Primal as a Complete Anatomy Learning Resource
- Enter a Gross Anatomy Lab with Confidence
Restricted lab time is no longer an issue with our 3D digital anatomy model. Reconstructed from real CT cadaveric data, our anatomy is medically accurate. Allowing you to perform dissections multiple times both in and outside the lab, out product gives you confidence in your learning. - Multimedia for Any Learning Style
Our movies, illustrations, functional and biomechanical animations promote understanding of core concepts in both anatomy and physiology. Along with our 3D model, this variety of multimedia delivers results whatever your learning style. - Assessments to Track Learning
Want to increase knowledge retention and assess student progress accurately? Our Perceptual and Adaptive Learning Modules (PALMs) are scientifically proven to reinforce learners’ grasp of essential anatomy concepts. Powered by patented technology that customizes learning to the individual, they also boast a sophisticated ‘Score Reporter’ facility that enables you to track and measure performance. - Anatomy is not just about learning names and identifying structures. It also involves understanding and interpreting abnormal anatomy and its relationship to diseases, disorders and injuries. Our resources present normal and abnormal anatomy, including anatomical variation, to lay the foundations for applying your knowledge to real-life clinical concepts and scenarios.
- Peer Reviewed for Excellence
All text in our products uses the widely respected Gray’s Anatomy as reference and our anatomy and physiology objectives are in alignment with the Human Anatomy and Physiology Society Learning Outcomes. Our team of inhouse anatomists writes this text and reviews and helps build each product. We also partner with experts in different clinical fields to ensure the content of each product is focused, accurate and current.